Looking to boost your Vue app’s text input beyond the basics? While plain textareas handle simple input, they quickly fall short when users need to format text, insert links, or embed media. This is where a powerful, feature-rich editor comes in. By upgrading your Vue textarea, you unlock creative possibilities and improve user engagement.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through five straightforward steps to integrate TinyMCE into your Vue textarea. From setup to plugin customization, you’ll have a fully functional WYSIWYG editor up and running in no time. Let’s dive in and take a basic Vue app to the next level!
Why you should upgrade your Vue textarea with a rich text editor
Plain Vue textareas are functional for simple input, but they quickly fall short when it comes to usability and versatility. If your users need to format their text, embed media, or add links without resorting to HTML, a rich text editor offers a better solution.
Key benefits of using a rich text editor in Vue
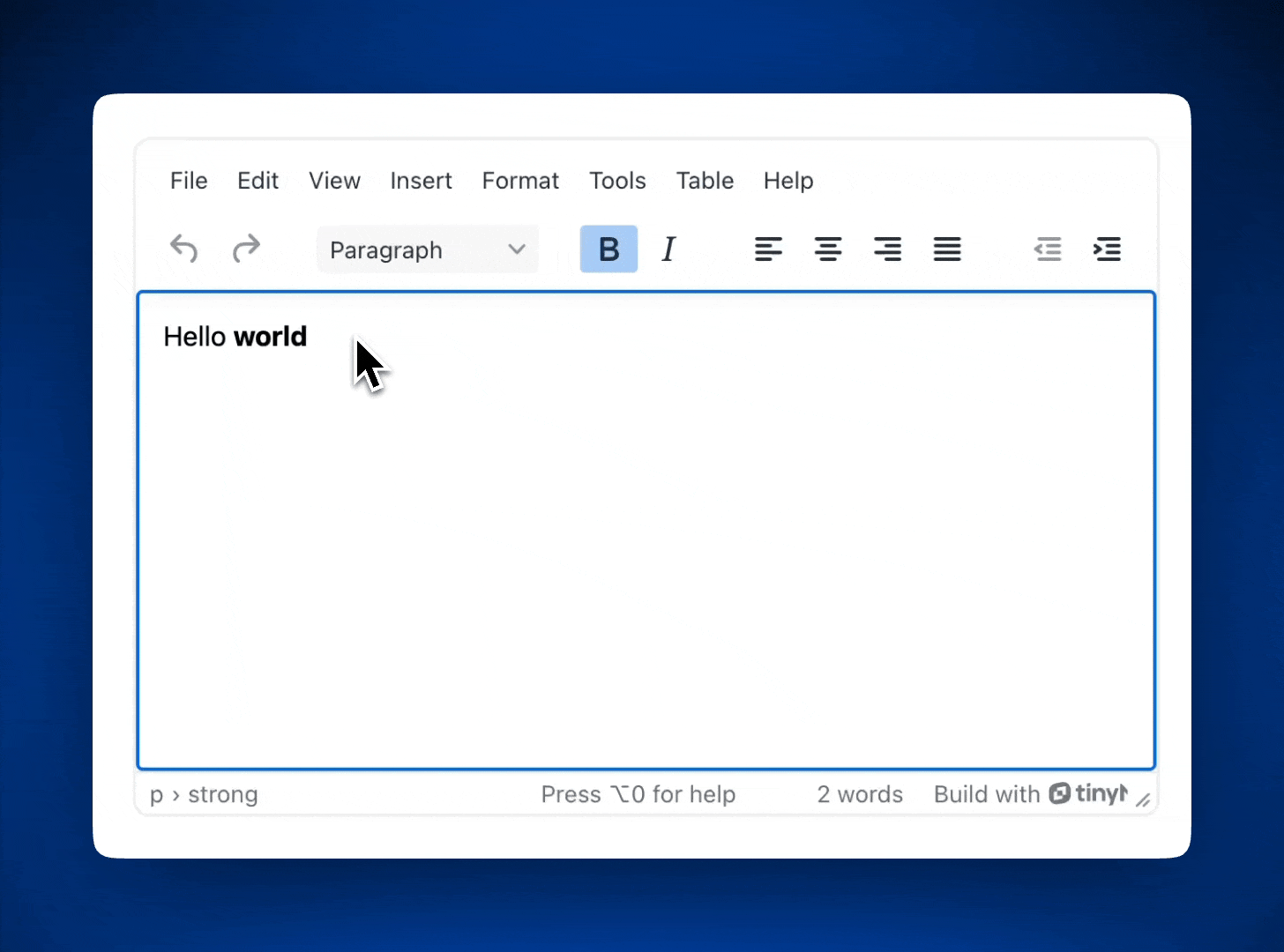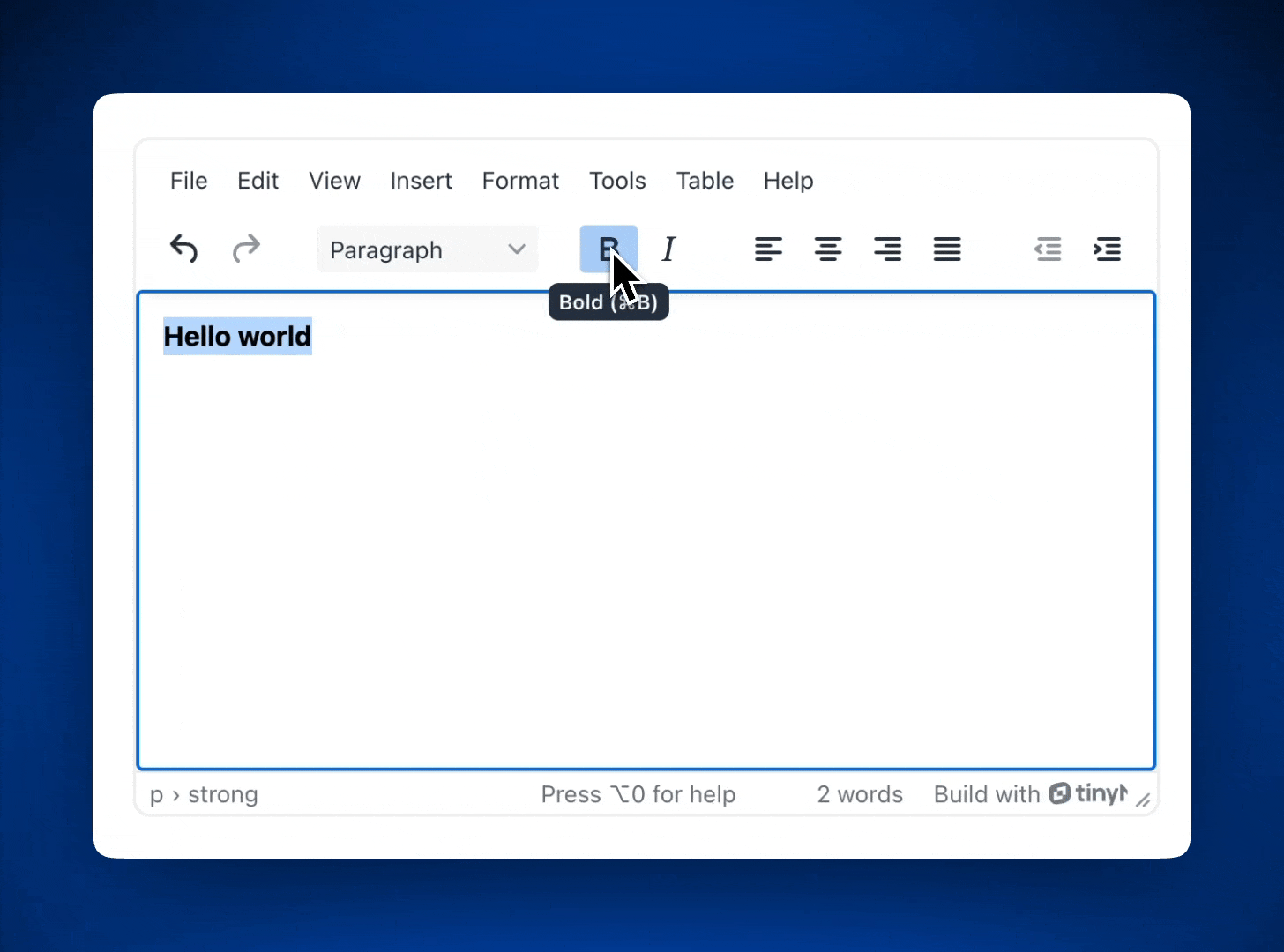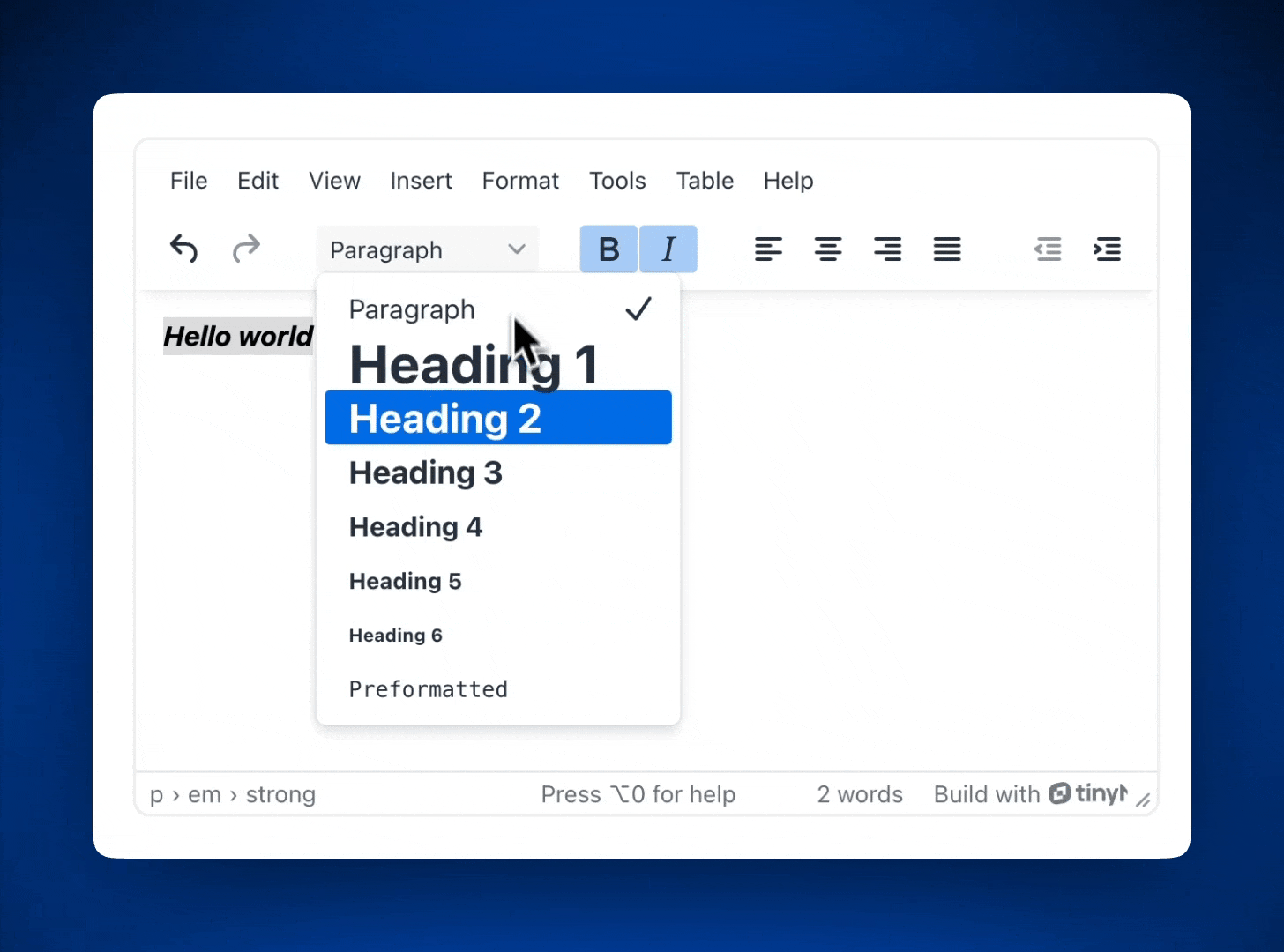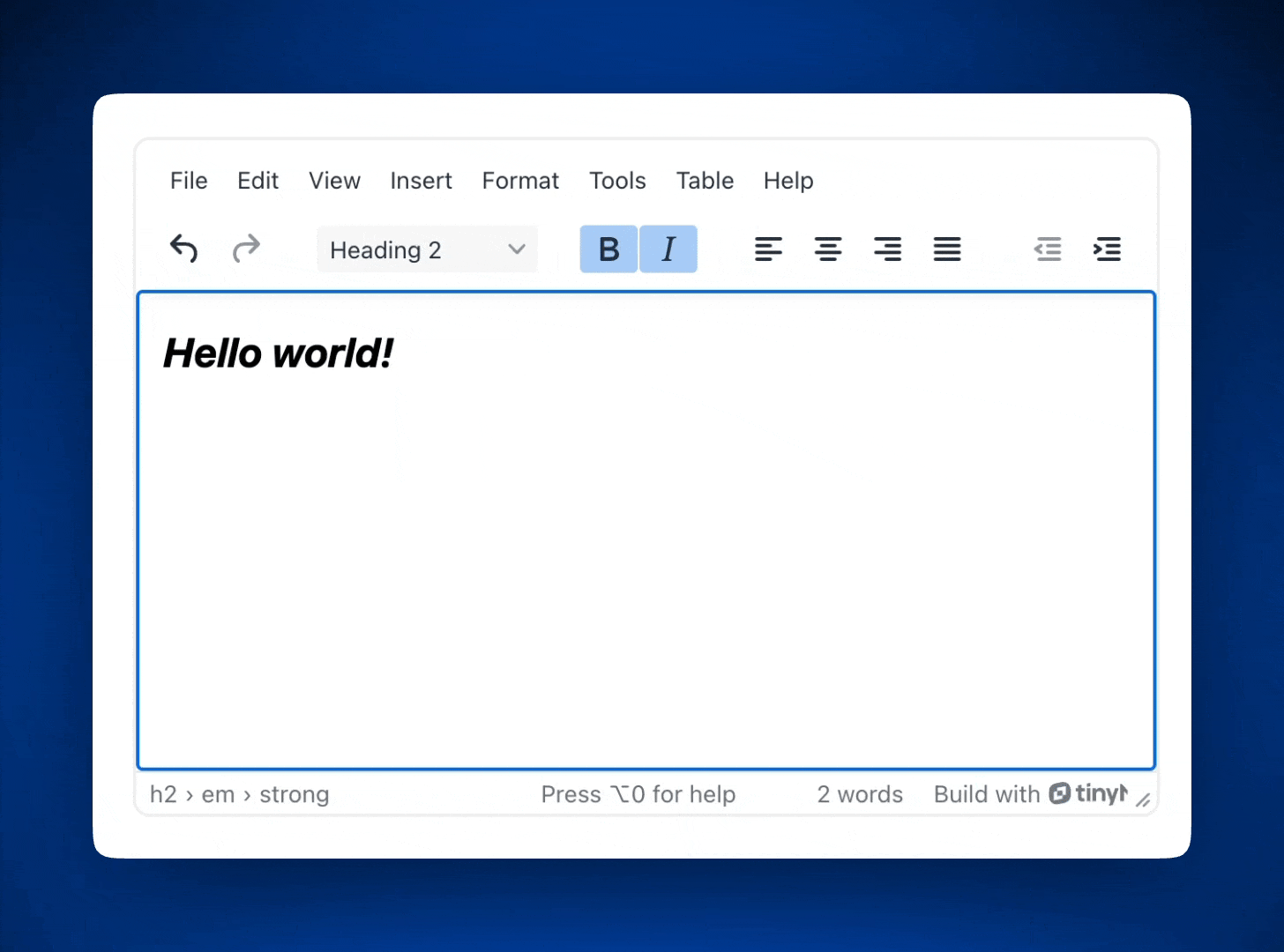
- User-friendly formatting: TinyMCE provides a clean interface with familiar tools (like bold, italics, and lists) that make writing intuitive for non-technical users.
- Consistent content structure: With built-in validation and formatting rules, you ensure that content stays organized and matches the required style (e.g., for blogs or reports).
- Seamless API integration: TinyMCE supports two-way binding through Vue's
v-model, allowing real-time data synchronization between the editor and your backend. - Media support: Easily embed images, tables, or links directly from the editor, removing the need for complex input forms or external upload tools.
- Customizability: TinyMCE offers plugins for specific needs, such as word counts or accessibility checks, giving you control over how users interact with the editor.
A basic Vue textarea can’t provide these kinds of features without significant custom development. By using TinyMCE, you reduce both the development effort and user friction while ensuring a smoother content creation experience.
In short, integrating a rich text editor into your Vue textarea ensures better usability, content consistency, and development efficiency—saving time for both developers and end-users.
Step one: Set up a Vue project
First, we need to create a Vue project. If you don’t have Vue installed yet, run the following command:
npm init vue@latestYou’ll be prompted with configuration questions. We recommend the following setup for this demo:
- Project name: tinymce-demo-vue
- Add Typescript? Yes
- Add JSX support? Yes
- Add Vue Router? Yes
- Add Pinia for state management? No
- Add Vitest for unit testing? No
- Add an E2E testing solution? No
- Add ESLint? Yes
- Add Prettier? Yes
- Vue DevTools extension? No
Once your project is configured, run these commands to navigate to the project folder and install dependencies:
cd tinymce-vue-demo
npm installWell done! Now that all our primary dependencies are installed, let’s install TinyMCE.
Step two: Add TinyMCE to the Vue project
To integrate TinyMCE into your project, install the official Vue package with:
npm install "@tinymce/tinymce-vue" --saveIt was that easy! Now let’s add the Editor to the Vue textarea so it will show up in the browser and be a usable demo.
Open your IDE and navigate to the App.vue file under the src folder. To add the WYSIWYG editor to our Vue textarea we’ll replace everything in the file with this code:
<script setup lang="ts">
import Editor from '@tinymce/tinymce-vue'
const apiKey = import.meta.env.VITE_TINYMCE_API_KEY // All Vite secret keys must begin with "VITE"
</script>
<template>
<Editor :api-key="apiKey" />
</template>Handle your TinyMCE API key securely
For security, store your API key in a .env file to keep it out of the main codebase. Create a .env file in your project directory with this content:
VITE_TINYMCE_API_KEY = "no-api-key";
👉Note: Make sure to replace "no-api-key" with a valid key, which you can obtain with a free 14-day TinyMCE trial. This setup ensures your API key won’t appear in production code.
Test your Vue project
With everything configured, start your development server:
npm run devVisit http://localhost:5173/ in your browser to see your app running with the TinyMCE editor right in your Vue textarea. Great job so far!
Step three: Add input binding to the textarea
In Vue, it’s important to bind our input fields to JSON objects when we GET and SET content via an API. For today’s demo, we’re going to add some input binding to TinyMCE so that it contains the content in our form.
Vue has a fantastic two-way binding component called v-model. V-model already does the work behind two-way binding for a field. All we need to do is:
- Add the
v-modelcomponent to ourEditor, and - Create a constant variable called “
content” that will reference our JSON object
In this guide, instead of a JSON object reference, we’ll put in some HTML as our content. Replace your current App.vue with this:
<script setup lang="ts">
import Editor from '@tinymce/tinymce-vue'
import { ref } from 'vue'
const apiKey = import.meta.env.VITE_TINYMCE_API_KEY
const content = ref('Hello <strong>world</strong>')
</script>
<template>
<Editor :api-key="apiKey" v-model="content" />
</template>In the real world, the “ref” value will change based on the data returned by your API call. This is a reactive field that can already GET and SET because of v-model’s two-way binding. This is part of the Composition API’s capabilities in Vue.
Step four: Add some useful rich text editor plugins
If you’d like a few basic plugins like rich text formatting, indentation, undo and redo, and advanced text styles, replace the code in App.vue with this configuration for TinyMCE.
<script setup lang="ts">
import Editor from '@tinymce/tinymce-vue'
import { ref } from 'vue'
const apiKey = import.meta.env.VITE_TINYMCE_API_KEY
const content = ref('Hello <strong>world</strong>')
</script>
<template>
<Editor :api-key="apiKey" v-model="content"
:init="{
plugins: 'lists link image table code help wordcount',
toolbar: 'undo redo | blocks | bold italic | alignleft aligncenter alignright alignjustify | outdent indent'
}"
/>
</template>Now we have a really nice rich text editor with some formatting options in our demo. Let’s get in the sandbox and see what we made!
Step five: Test your new Vue app
Your Vue app instance should still be running on http://localhost:5173/, so there’s no need to run the server again. Just save your App.vue file with this new plugin configuration and visit the link.
👉 Note: Don’t forget to replace “no-api-key” with your real API key inside your .env file.
If you added the plugins in step four, our Vue app with TinyMCE will look like this:
Ready to level up?
Once you’ve integrated TinyMCE, there are endless ways to enhance your editor. Here are more Vue resources to explore:
- The best rich text editors for Vue
- How to enable upload image with Vue
- Migrating from Tiptap to TinyMCE: the Vue.js configuration
- How to set up a Vue emoji picker
- Mastering Font Awesome in Vue.js
- How to set up Vue fonts in your WYSIWYG
- Angular vs React vs Vue - Detailed Framework Comparison
TinyMCE offers a versatile ecosystem of plugins and customization options to fit your needs. There’s always room to take your editor further. Find out more about us on the TinyMCE YouTube channel or follow TinyMCE on X (formerly Twitter) to let us know how you’re using TinyMCE.
